Carolina Quayle
From DNA Repair Lab
| Revision as of 19:10, 12 July 2007 Cquayle (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 14:06, 25 November 2011 Root (Talk | contribs) Next diff → |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {| align="left" | + | {| |
| - | |[[Image:.jpg|150px|left]] | + | |- |
| + | |[[Image:Primária.jpg|150px]] | ||
| + | |Graduated Biologist and licenced teacher by University of São Paulo (USP) in 2006 and 2009, respectively. PhD student in the Microbiology Department of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences – USP, developing the project entitled “The effect of ultraviolet radiation induced DNA lesions in MEFs and mice knockout for DNA repair genes”. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan=2| | ||
| - | {| align="left" cellspacing="2" width="50%" heigh="30%" | ||
| - | |valign="top" style= "background-color: #F8F8FF; border: 1px solid #CAE1FF; padding: 10px"| | ||
| - | Graduated in Biological Sciences in Universidade de São Paulo (USP) in 2006.Now she is developing a PhD project in mutagenesis: "Analysis of the effect of CPD and 6-4PP DNA lesions induced by ultraviolet light in NER deficient mice".''' | ||
| - | |} | ||
| - | |} | ||
| - | == Research abstract == | ||
| - | DNA lesions, if not corrected, may result in mutations, cell death and cancer. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the most carcinogenic exogenic factor in our environment nowadays, causing mostly cyclobutane pirimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6-4 pirimidine-pirimidone photoproducts (6-4PPs). Photolyases are enzimes capable of reverting these lesions in a specific and direct way, using visible light as source of energy. Placental mammals lack these enzymes and dispose only of nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway to remove double-helix distorting lesions. Despite the extensive research that has been done, in vitro and in vivo, the role of each lesion in apoptosis, tumorigenesis, edema and other effects induced by UV light is still unclear. Based in the results obtained with cells profficient and defficient in different repair genes and in mice profficient in DNA repair, we suggest that in individuals proficient in all DNA repair genes, CPDs lesions are responsible for cancer induction since its removal its slower. Thus, in NER defficient individuals, 6-4PP lesions must be responsible for the vast majority of the UV effect since it is a more helix-distorcing lesion. Since all in vivo experiments have used DNA repair proficent mice, we suggest the development of experiments using mice defficient in the NER pathway. Nockdown mice in the XPA and XPC genes of the NER pathway present a similar phenotype to xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) patients, including hipersensibility to UV light with increased risk of cancer. The goal of this work is to analyse the role of CPD and 6-4PP lesions in vivo, using XP mice transduced with specific photolyase in an adenoviral vector, treated with UVB radiation. Preliminary data suggests shows protection in both groups. | ||
| - | == Finantial support== | + | == Research Project == |
| - | FAPESP | + | |
| - | == Selected publications == | + | The ultraviolet (UV) component of the sun is the most abundant genotoxic factor present in the environment, inducing two types of photolesion on DNA: the cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) and the pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproduct (6-4PP). Photolyases are enzymes capable of using the energy of a photon of light to directly convert these dimers back to monomers. These enzymes are absent in placental mammals that count only with the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway to remove these double-helix distorting photolesions. Deficiencies in genes involved in this pathway lead to the development of severe syndromes, such as Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP). Patients with this condition show high photosensitivity and a substantial increase in skin cancer incidence in sun exposed areas. Despite the extensive research that has been done “in vitro” and “in vivo”, the specific role of each photolesion in local e systemic responses such as edema, erythema, apoptosis, tumorigenesis and immunosuppression is still unclear. Based on previous data, from cells proficient and deficient in DNA repair and mice deficient in DNA repair, we suggest that in DNA repair proficient individuals CPD lesions are mostly responsible for tumor induction due to its slow repair. In DNA repair deficient patients 6-4PP lesions must also play an important role due to its bigger double-helix distortion. This project aims to define “in vivo” the specific role of each photolesion in local and systemic responses to UV radiation. To that end XPA knockout mice that constitutively express either CPD-photolyase or 6-4PP-photolyase are daily irradiated with a low UVB dose and their responses are analyzed. |
| - | Mercuri LP, Carvalho LV, Lima FA, '''Quayle C''', Fantini MC, Tanaka GS, Cabrera WH, Furtado MF, Tambourgi DV, Matos Jdo R, Jaroniec M, Sant'Anna OA. Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15: a new effective adjuvant to induce antibody response. '''Small''', 2(2):254-6, 2006. | + | <br> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | http://www.icb.usp.br/~mutagene/images/thumb/5/51/FiguraQuayle.jpg/350px-FiguraQuayle.jpg | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Figure - The effects of photorepair of CPDs and 6-4PPs on UV-induced apoptosis: in NER proficient individuals only CPD removal reduces apoptosis whereas in NER deficient cells CPD and 6-4PP removal is capable of reducing the apoptotic response (adapted from reference 1). | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Main publications== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1- '''Quayle C''', Menck, CFM, Lima-Bessa, KM (2011) Recombinant viral vectors for investigating DNA damage responses and gene therapy of Xeroderma Pigmentosum. Chapter 6. In '''DNA Repair and Human Health''', ISBN 978-953-307-612-6, edited by Sonya Vengrova, InTech - Open Access Publisher, 145-174. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2- Eker AP, '''Quayle C''',Chaves I, van der Horst GT. DNA repair in mammalian cells: Direct DNA damage reversal: elegant solutions for nasty problems. '''Cellular and molecular life sciences''', 66(6):968-80, 2009. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3- da Costa RM, '''Quayle C''', de Fátima Jacysyn J, Amarante-Mendes GP, Sarasin A, Menck CF.Resistance to ultraviolet-induced apoptosis in DNA repair deficient growth arrested human fibroblasts is not related to recovery from RNA transcription blockage.'''Mutation Research''', 640(1-2):1-7, 2008. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4- Mercuri LP, Carvalho LV, Lima FA, '''Quayle C''', Fantini MC, Tanaka GS, Cabrera WH, Furtado MF, Tambourgi DV, Matos Jdo R, Jaroniec M, Sant'Anna OA. Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15: a new effective adjuvant to induce antibody response. '''Small''', 2(2):254-6, 2006. | ||
Revision as of 14:06, 25 November 2011
| Graduated Biologist and licenced teacher by University of São Paulo (USP) in 2006 and 2009, respectively. PhD student in the Microbiology Department of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences – USP, developing the project entitled “The effect of ultraviolet radiation induced DNA lesions in MEFs and mice knockout for DNA repair genes”.
|
|
Research ProjectThe ultraviolet (UV) component of the sun is the most abundant genotoxic factor present in the environment, inducing two types of photolesion on DNA: the cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) and the pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproduct (6-4PP). Photolyases are enzymes capable of using the energy of a photon of light to directly convert these dimers back to monomers. These enzymes are absent in placental mammals that count only with the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway to remove these double-helix distorting photolesions. Deficiencies in genes involved in this pathway lead to the development of severe syndromes, such as Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP). Patients with this condition show high photosensitivity and a substantial increase in skin cancer incidence in sun exposed areas. Despite the extensive research that has been done “in vitro” and “in vivo”, the specific role of each photolesion in local e systemic responses such as edema, erythema, apoptosis, tumorigenesis and immunosuppression is still unclear. Based on previous data, from cells proficient and deficient in DNA repair and mice deficient in DNA repair, we suggest that in DNA repair proficient individuals CPD lesions are mostly responsible for tumor induction due to its slow repair. In DNA repair deficient patients 6-4PP lesions must also play an important role due to its bigger double-helix distortion. This project aims to define “in vivo” the specific role of each photolesion in local and systemic responses to UV radiation. To that end XPA knockout mice that constitutively express either CPD-photolyase or 6-4PP-photolyase are daily irradiated with a low UVB dose and their responses are analyzed.
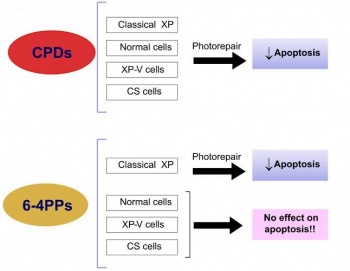
Figure - The effects of photorepair of CPDs and 6-4PPs on UV-induced apoptosis: in NER proficient individuals only CPD removal reduces apoptosis whereas in NER deficient cells CPD and 6-4PP removal is capable of reducing the apoptotic response (adapted from reference 1).
Main publications1- Quayle C, Menck, CFM, Lima-Bessa, KM (2011) Recombinant viral vectors for investigating DNA damage responses and gene therapy of Xeroderma Pigmentosum. Chapter 6. In DNA Repair and Human Health, ISBN 978-953-307-612-6, edited by Sonya Vengrova, InTech - Open Access Publisher, 145-174. 2- Eker AP, Quayle C,Chaves I, van der Horst GT. DNA repair in mammalian cells: Direct DNA damage reversal: elegant solutions for nasty problems. Cellular and molecular life sciences, 66(6):968-80, 2009. 3- da Costa RM, Quayle C, de Fátima Jacysyn J, Amarante-Mendes GP, Sarasin A, Menck CF.Resistance to ultraviolet-induced apoptosis in DNA repair deficient growth arrested human fibroblasts is not related to recovery from RNA transcription blockage.Mutation Research, 640(1-2):1-7, 2008. 4- Mercuri LP, Carvalho LV, Lima FA, Quayle C, Fantini MC, Tanaka GS, Cabrera WH, Furtado MF, Tambourgi DV, Matos Jdo R, Jaroniec M, Sant'Anna OA. Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15: a new effective adjuvant to induce antibody response. Small, 2(2):254-6, 2006. |
|